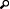- Contents
ACD Processing Technical Reference
Types of ACD
On the Configuration tab of the Workgroup Configuration dialog box, you can specify the type of ACD routing to use by selecting the appropriate item from the Workgroup has Queue list. Definitions of the ACD types appear below.
- Custom
-
With custom ACD processing, agents and interactions each receive scores in various categories. CIC processes the scores to determine The scores are processed to determine the agents who are qualified to handle each interaction. Interactions are assigned to the available agent with the highest acceptable score. For more information about using custom ACD processing, see
Configuring Customer Interaction Center’s ACD Processing
. - Group Ring
- This setting alerts all available members of a workgroup simultaneously
when an interaction is available in the queue for that workgroup.
Selecting group ring disables the Agent Utilization, ACD Skills, and ACD Actions functions (the items on those tabs are not available). The Workgroup Offering Call Timeout setting determines the length of the group ring.
Note:
Group ring only works with queues that only handle telephone calls. You cannot use group ring with chats, email, social conversations, direct messages, or generic objects. - Sequential
- This setting alerts individual members of a workgroup that a new
interaction is available in the queue for that workgroup.
Members are alerted to the call in the order specified in Workgroup Configuration properties > Members page under Currently Selected Users. Every time an interaction comes in, the users are alerted in the listed order.
Selecting Sequential disables the Agent Utilization, ACD Skills, and ACD Actions functions (the items on those tabs are not available). The Workgroup Offering Call Timeout setting determines the length of the sequential ring.
Note:
Only telephone calls can alert hunt groups. Hunt groups are not usable with chats, email, social conversations, direct messages, or generic objects.
- Round-robin
- Similar to linear hunt groups, the round robin feature remembers
the last user who was sent a call. Round robin works in a loop, repeating
the process down through the list, and then the process starts over
with the next call.
For example, a workgroup has three users (User1 - User3), all available for workgroup calls and listed as User1, User2, User3, in that order. If User1 received the last call but is available, the next alerting call goes to User2. The next alerting call after that goes to User3 if that user is available.
Selecting Round Robin disables the Agent Utilization, ACD Skills, and ACD Actions functions (the items on those tabs are not available). The length of the Round robin ring is determined by the Workgroup Offering Call Timeout setting.
Note:
Only telephone calls can alert hunt groups at this time. Hunt groups cannot be used with chats, emails, social conversations, direct messages, or generic objects. - ACD
-
This ACD routing type is a simplified form of ACD routing available in Interaction Administrator. It routes interactions based solely on each agent’s time available. With this option, skills assigned to an agent or interaction by the ACD Specify Skill tool are only considered if the workgroup requires certain skills and proficiencies. Otherwise, all agents and interactions effectively have equal scores in all skills, so new interactions go to the agent with the longest available time. If an interaction comes in when no agents are available, it goes to the first agent that becomes available.
Note:
When ACD Server subsystem evaluates a call’s skills, it first looks for skills that were explicitly assigned to that agent from Interaction Administrator. If the required skills were not explicitly assigned, ACD Server looks at the skills that the agent inherited from any workgroups to which he or she belongs. CIC uses the agent’s entire set of skills is used to evaluate an interaction on a workgroup queue. - Bullseye
-
Bullseye routing, which is available only with a custom workgroup, assigns interactions to agents based on selection pools. Picture a target with a bullseye in the center and four rings around the bullseye. One or more agents are assigned to the bullseye (ring 1) and to each of the rings, 2-5, outside of the bullseye. Each ring has a configured timeout.
Bullseye routing is not configurable from workgroup configuration. You assign agents and a timeout to each ring using the ACD Initiate Bullseye Processing tool in Interaction Designer. Assign the preferred agents to ring 1, the bullseye, so they are considered first. For more information about the tool, see ACD Initiate Bullseye Processing in the Interaction Designer help.
When processing an interaction, ACD Server first attempts to assign the interaction to an agent in the bullseye selection pool. If none of the agents in that pool are available before the timeout, ACD Server then widens the selection pool to include the next ring. The selection pool continues to widen if ACD Server does not find an available agent. If a ring does not contain any agents who are logged in, ACD Server skips that ring without waiting for the timeout.
Once it exhausts all of the rings, ACD Server reverts to normal ACD processing where the selection pool includes any agent in the ACD workgroup.
When two or more agents are available, ACD Server bases the selection on the agent with the longest available time.
Notes:
-
When two or more agents are available, ACD Server selects the agent with the longest available time.
-
If two or more interactions are available when an agent logs in, ACD Server considers their priority and then the longest wait time.
-