- Contents
Interaction Web Tools Technical Reference
Interaction Web Tools Network Architecture
The following information describes the Interaction Web Tools architecture and the roles of the different servers and of the visitor's browser. The illustration shows the architecture of the Interaction Web Tools network. It consists of the following computers:
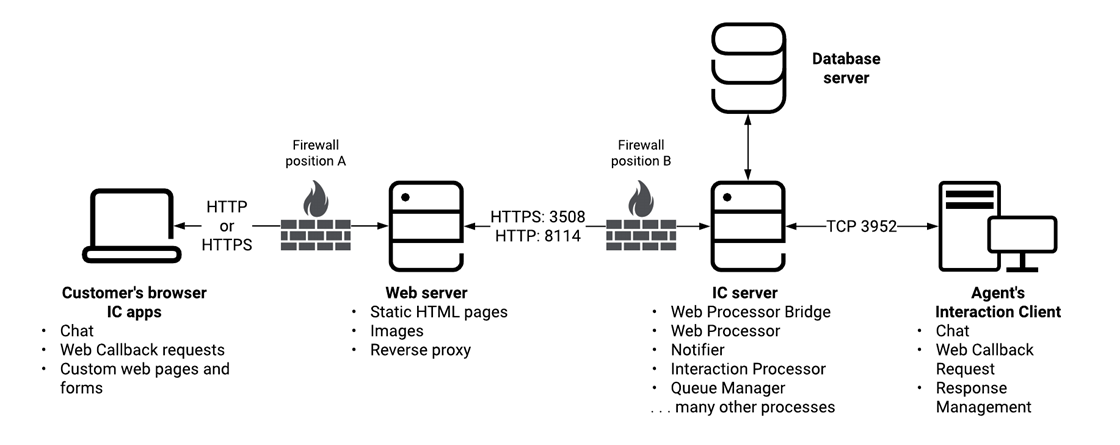
Web server
The web server runs Microsoft IIS or other compatible web server software and connects to the CIC server over port 3508 (HTTPS) and 8114 (HTTP). The default port numbers are 3508 and 8114, but you can configure other port numbers. You can enable either HTTPS or HTTP or both.
CIC server
The CIC server runs various other subsystems including WebProcessorBridge, WebProcessor, Notifier, Interaction Processor, and Queue Manager. The visitor's browser tells Interaction Web Tools to send data, to create and manage chats and callback requests on agent and workgroup queues, and (optionally) to create visitor registration records. Interaction Web Tools is similar to Telephony Services. The difference is that it generates and controls web interactions instead of telephone interactions. The WebProcessorBridge communicates to the WebProcessor on the CIC server to create and manipulate objects and events.
WebProcessor
-
Sends requests to other CIC components.
-
Manages intercom chats between internal CIC Client users residing on the same CIC server.
-
Creates and controls web chat sessions between website visitors users and your agents.
-
Manages callback requests started by visitors to your website.
WebProcessorBridge
-
Registers visitors by creating Interaction Tracker records.
-
Authenticates website visitors by looking up their visitor name and password in the Interaction Tracker tables.
-
Forwards callback requests to WebProcessor.
Web HTML plug-in
This plug-in resides on the CIC server. It processes requests and responses between the web server and the CIC server. For example, you can employ a custom handler to enable your website visitors to query a particular agent's availability before starting a chat or making a callback request.
-
The web server sends a request to the Web HTML plug-in on the CIC server.
-
The CIC server invokes a custom handler which processes the request.
-
The handler passes the result to the Web HTML plug-in which formulates a response and sends it to the web server.
-
The web server forwards the response to the visitor.
Database server
When visitors register on your website, Interaction Tracker tables store their registration information. The database configuration portion of the CIC installation creates these tables and prompts you to select a reporting package to create these tables.
Visitor's Browser
Visitors connect to your website and start web interactions. The interactions are queued and processed similarly to telephone calls, including ACD processing. You can enable access to one or more interaction types either through the default released version of handlers, or through custom pages that adopt your site's look and feel. You can create software to send the same types of messages that the visitor's browser sends in a standard installation and start web interactions. Your custom applications can include this functionality. For more information about customizing the Interaction Web Tools interface, see the Interaction Web Tools Developer's Guide at https://help.genesys.com/cic/mergedProjects/wh_tr/desktop/pdfs/web_tools_dg.pdf.
Agent's CIC client
Through the CIC client, agents can monitor and control the various web interaction types. These actions are achieved through the following features:
-
Chat
-
Web Callback request
-
Response Management
Registration and authentication
Interaction Web Tools registers and authenticates visitor information it stores in Tracker tables on the CIC server. Setup Assistant creates these Tracker tables as part of the database configuration.