- Contents
SSO Identity Providers Technical Reference
Secure Token Server validation digital certificate
This certificate, if signed authentication requests are required by the identity provider, is embedded within SAML <AuthnRequest> messages.Each identity provider may have differing configurations and requirements.As such, you may need to provide the Secure Token Server validation certificate to the identity provider, even if it does not require signed authentication requests.
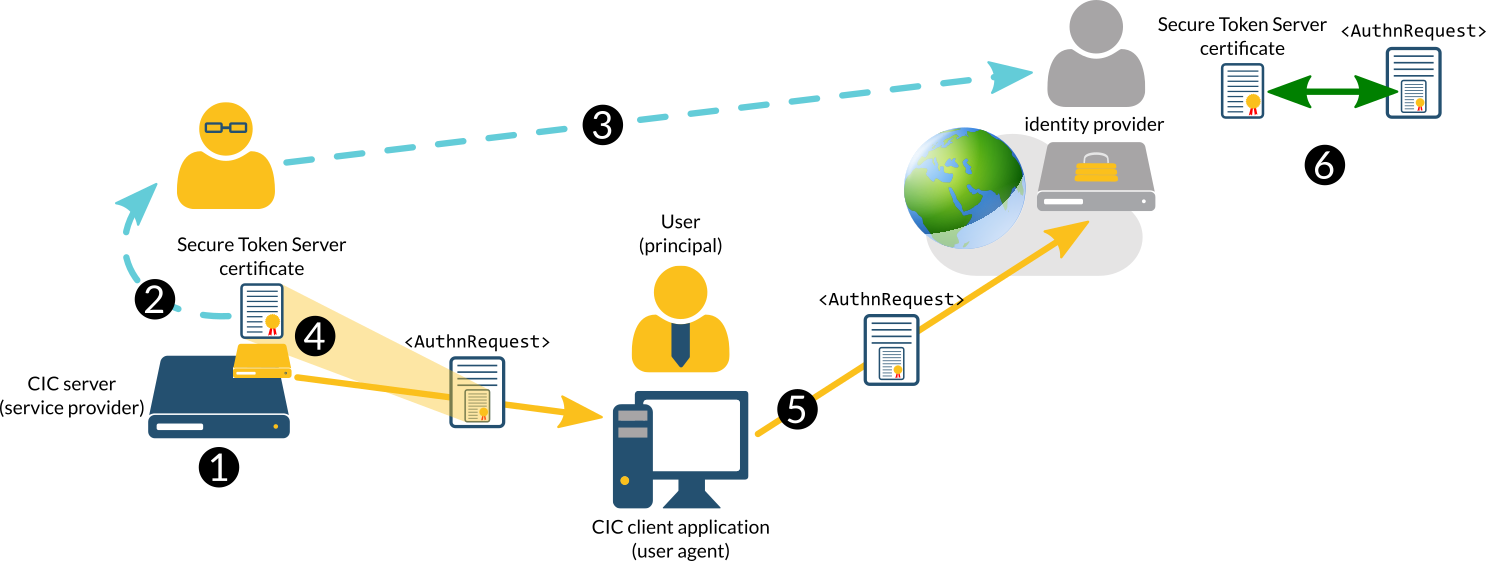
The following diagram shows how a CIC Single Sign-On environment uses Secure Token Server validation certificates:
|
Step |
Description |
|
1 |
The CIC server, as a Single Sign-On service provider, generates a certificate for the Secure Token Server subsystem with which it can sign SAML <AuthnRequest> messages. |
|
2 |
The administrator copies the Secure Token Server certificate from the CIC server. |
|
3 |
The administrator sends the Secure Token Server certificate to the identity provider. |
|
4 |
For signed SAML <AuthnRequest> messages, the Secure Token Server subsystem embeds the certificate in the message and sends it to the user agent when it requests authorization. |
|
5 |
The user agent sends the SAML <AuthnRequest> message, which contains the certificate, to the identity provider. |
|
6 |
The identity provider compares the certificate in the <AuthnRequest> message with the one that was previously provided by the administrator to determine if it can be trusted.If the certificate can be trusted, the identity provider then processes the SAML <AuthnRequest> message and attempts to validate the principal. |



