AIM Help
AIM help provides you with information for using AIM. To locate and view a topic, use the table of contents, index, and search features.
To open help
In menu bar, click the Help option and then click Help on AIM. The AIM Help window appears.

Tip: To adjust the width and height of the window or its panes, click the edge of the window or pane and drag it up or down, left or right.
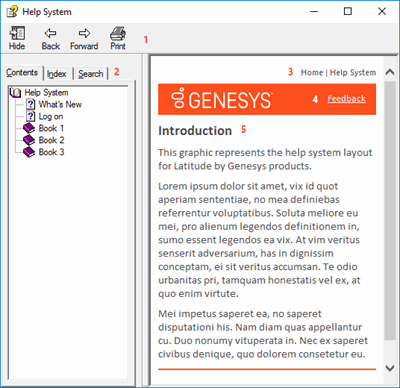
Toolbar: Allows you to hide or show tabs and the Navigation pane, move forward and backward through topics, and print the currently displayed topic.
Tabs: Displays the following:
Contents: Displays the table of contents. To display a topic in the Content pane, expand a book and then click the link.
Index: Displays the index. To display a topic in the Content pane, type a keyword or phrase in the box (or scroll through the list) and then click the link in the list.
Search: Displays the search feature. To display a topic in the Content pane, type a keyword or phrase in the box and then press Enter. In the search results, click the link.
Glossary: If available, displays a list of terms and their definitions. To display a definition, click the term.
Breadcrumbs: Displays your current location within the help system. When you click a breadcrumb, the related topic displays.
Content toolbar: Displays an option to send feedback through an email message to Latitude by Genesys Documentation.
Content pane: Displays the contents of a topic. To view the Content pane menu, right-click in the Content pane.
You can use the search feature to search for topics that contain words or phrases that you specify. You formulate a search query following a specific set of rules. You can include wildcard expressions, Boolean operators, and nested expressions in your search query. A list of topics that match your search criteria appear in the search results. When you click a topic title in the search results, the content of that topic appears in the Content pane.
The basic rules for formulating search queries are:
Searches are not case-sensitive, meaning you can type uppercase or lowercase characters.
You cannot search for a single character or the following reserved words: an, and, as, at, be, but, by, do, for, from, have, he, in, it, not, of, on, or, she, that, the, there, they, this, to, we, which, with, you.
The search engine ignores punctuation marks and special characters such as @#$%^&()=+[]\.
Enclose phrases and terms that include a period (such as a file name with an extension) in double quotation marks.
Wildcard expressions allow you to search for one or more characters using a question mark or asterisk. A question mark represents a single character, while an asterisk represents one or more characters.
Search for... |
Example |
Result |
Topics with text that starts with one or more specified characters and ends in any character or number of characters |
log or log* |
Returns all topics with text that starts with the specified characters (for example, log, logon, logging). |
Topics with text that starts with the specified characters, has a single character that can be anything, and ends in the specified characters |
32?57 |
Returns all topics with text that has any character where you placed the question mark (for example, 32?57 returns 32257, 32457, and 32857). |
Topics that contain all the words specified, in any order or placement within the topic |
account status |
Returns all topics with both account and status, but not necessarily as a phrase or in the order specified. For example, the search returns topics with "the account status..." or "the status of the account..." |
Topics that contain the specified phrase |
"account status" |
Returns all topics with account status as a phrase. For example, the search returns topics with "the account status..." but not "the status of the account..." |
Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT, NEAR) allow you to create a relationship between terms. If you don't specify an operator, the system uses AND by default.
Search for... |
Example |
Result |
AND |
account AND status |
Returns all topics with both account and status, but not necessarily as a phrase or in the order specified. For example, the search returns topics with "the account status..." or "the status of the account..." |
OR |
account OR status |
Returns all topics with either account or status, or both. |
NOT |
account NOT status |
Returns all topics with account but not status. |
NEAR |
account NEAR status |
Returns all topics where account is within eight words of status. |
Nested expressions allow you to perform complex searches. For example, queue AND ((collector OR clerical) not supervisor) finds topics containing queue and collector but not supervisor, or containing queue and clerical but not supervisor. As with mathematical expressions, the system evaluates expressions in parentheses first. If there is no parenthesis, the system evaluates the expression from left to right. For example, queue NOT (clerical OR supervisor) finds topics containing queue but not clerical or supervisor. Queue NOT clerical OR supervisor finds topics containing queue but not clerical, or topics containing supervisor.