- Contents
Interaction Media Server Technical Reference
Configure Network Interfaces on Interaction Media Server
Interaction Media Server can use one or more network interfaces on the host computer. Interaction Media Server packaged servers provide multiple network interfaces.
If available, use multiple network interfaces with Interaction Media Server. With multiple interfaces available, Interaction Media Server can do its own load balancing by selecting different network interfaces for Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) streams.
Also, using multiple network interfaces in your Interaction Media Servers enables you to connect them to different networks and hardware, which can eliminate single-point-of-failure scenarios, such as a network interface or switch becoming inoperative.
You can control multiple network interfaces in an Interaction Media Server host through the following Interaction Media Server properties.
-
RtpLocalAddress
-
RtpLocalAddressMass
Through a combination of these properties, you can specify a range of addresses for network interfaces that Interaction Media Server can select for RTP communications. For more information about these properties, see Interaction Media Server Config-Properties Page.
Teamed network interfaces
Teamed network interfaces bind multiple interfaces to a single IP address. This teaming capability is available through either one of the following means:
-
Software designed specifically by the manufacturer for a specific network interface
-
Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, or Windows Server 2019 native functionality
Important!
Genesys testing has shown that network interface teaming in a load balancing configuration on Interaction Media Server results in the creation or increase of audio issues. Genesys does not support Interaction Media Server instances that use network interface teaming in a load balancing configuration.
You can use network interface teaming in a fault tolerance configuration. However, if you experience an increase in audio issues in such a configuration, Genesys recommends that you disable teaming and use the network adapters individually; with each having its own IP address.
For more information about configuring and using network interface teaming in a fault tolerance configuration, see the document for the software that you are using for that functionality.
Interaction Media Server provides its own form of load balancing when you specify multiple network interfaces on the host through usage of the RtpAddressLocal and RtpAddressLocalMask properties.
Configure Interaction Media Server for virtual local area networks
Some network environments use virtual local area networks (VLANs) to segregate different types of network traffic, such as voice and data, to ensure lower latency and to prevent the overloading of network entities, such as routers. Usually, a computer or server uses multiple network interface cards (NICs) to communicate with the separate VLANs.
Interaction Media Server enables you to direct Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) network communications through a specified NIC in the host computer. Use the RtpAddressLocal and RtpAddressLocalMask properties in the Interaction Media Server Config-Properties Page of the Interaction Media Server web interface. For the procedure to configure the RTP NIC binding for Interaction Media Server, see "Configure Interaction Media Server to use a network interface for RTP communications."
Routing of network messages through other protocols, such as SIP, HTTP, and Notifier, depends on the current configuration of the Windows routing table. For more information about the routing table in Windows, see http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc779122(v=ws.10).aspx. To modify the Windows routing table, use the route command in a command prompt. For more information about the route command, see http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff961510.aspx
The Windows routing table contains destination IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, a NIC IP address, and a metric value so that Windows can determine which NIC to use to send a network message. Windows does not consider the protocol of a network message when it uses the routing table to determine the NIC to use. For example, you cannot configure Windows to route Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) messages to use a specific NIC or VLAN; only through the IP address mask of the destination.
Tip:
If you need help configuring Interaction Media Server for specific behaviors with virtual local area networks, contact Genesys Professional Services by sending an email message to PSO2@genesys.com.
Note:
If you have not specified a network interface for the UdptlAddressLocal and UdptlAddressLocalMask properties, Interaction Media Server sends UDPTL packets for T.38 and T.30 faxing through the network interface specified in the RtpAddressLocal and RtpAddressLocalMask properties.
Configure Interaction Media Server to use a network interface for RTP communications
You can configure Interaction Media Server to send network communications containing RTP packets through a specific network interface on the host computer.
To configure Interaction Media Server to use a network interface for RTP communications
-
From a personal computer or the Interaction Media Server itself, open a web browser and navigate to the URL address and port number of the Interaction Media Server web interface. See the following example for the format of specifying this address:
http://mediaserver1.mydomain.com:8084/Note:
Packaged Interaction Media Servers use HTTP port 8083. Software-only installations of Interaction Media Server default to HTTP port 8084.
-
Log on to the Interaction Media Server configuration webpage with the administrative user ID and password. The Status-About page appears.
-
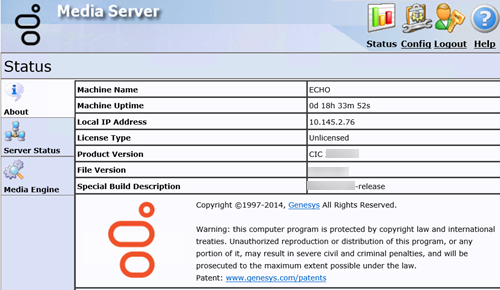
In the upper right corner, click the Config icon. The Config-Servers page appears.
-
On the left side of the page, click the Properties tab. The Config-Properties page appears.

-
In the Select or enter name of property list box, select RtpAddressLocal. The RtpAddressLocal property appears in the list of current properties.
-
In the Select or enter name of property list box, click RtpAddressLocalMask. The RtpAddressLocalMask property appears in the list of current properties.
-
In the RtpAddressLocal box, type the IP address for the local network interface to use to send communications containing RTP packets.
-
In the RtpAddressLocalMask box, type a valid subnet mask that specifies the range of valid IP addresses of local network interfaces that Interaction Media Server can use to send RTP packets.
Note:
If the host machine has multiple network interface cards (NICs), Interaction Media Server balances RTP network communications by randomly selecting a socket from a NIC that matches an IP address within the RtpAddressLocal and RtpAddressLocalMask values.
-
Click Apply Changes.