- Contents
PureConnect Quality of Service Technical Reference
Class Based Weighted Fair Queuing / Low Latency Queue CBWFQ/LLQ
On this page Hide
CBWFQ/LLQ is the best practice for implementing QoS on WAN networks at the core edge routers. The configuration is based on the assumption that you established trust boundaries on the network infrastructure and marked traffic at the access layer according to the following template:
|
Application/Protocol |
DSCP Marking |
CoS Value |
|---|---|---|
|
Voice traffic (RTP) PureConnect Notifier |
EF |
5 |
|
Recordings |
AF22 |
1 |
|
Bulk transfer traffic (Web/FTP/etc) |
AF11 AF12 AF13 |
1 |
|
Transactional applications (Databases etc) |
AF21 AF22 AF23 |
2 |
|
Mission critical applications (Core business traffic) |
AF31 AF32 AF33 |
3 |
|
Interactive video traffic |
AF41 AF42 AF43 |
4 |
|
IP routing (RIP, BGP, OSPF etc) |
CS6 |
6 |
|
Streaming video |
CS4 |
4 |
|
Voice/Video signaling (SIP, etc) |
CS3 |
3 |
|
Network management traffic (SNMP etc) |
CS2 |
2 |
|
Scavenger traffic |
CS1 |
1 |
|
Unclassified traffic |
CS0 (BE) |
0 |
This information concentrates on voice traffic only. All PureConnect voice endpoints can mark their packets. Assuming there are no QoS problems on the LAN side, the issue arises on the edge devices where bandwidth is limited when connecting to a service provider or any other edge device of another network.
Reclassification, queuing, and congestion avoidance using CBWFQ/LLQ with a WRED tail drop policy is the best recommended configuration for such a scenario. PureConnect products do not use WRED extensions such as ECN.
The following table outlines the best practices for reclassification, queuing, and congestion avoidance:
|
Application/Protocol |
Original DSCP Marking |
New DSCP Marking |
Drop Policy |
Queue used |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Voice traffic (RTP) PureConnect Notifier Traffic |
EF |
EF |
Not applied |
LLQ |
|
Recordings |
AF11 |
AF22 |
DSCP-based |
CBWFQ |
|
Bulk transfer traffic (Web/FTP/etc) |
AF11 AF12 AF13 |
AF22 |
DSCP-based |
CBWFQ |
|
Transactional applications (Databases etc) |
AF21 AF22 AF23 |
AF32 |
DSCP-based |
CBWFQ |
|
Mission critical applications (Core business traffic) |
AF31 AF32 AF33 |
AF31 |
DSCP-based |
CBWFQ |
|
Interactive video traffic |
AF41 AF42 AF43 |
CS4 |
DSCP-based |
LLQ |
|
IP routing (RIP, BGP, OSPF etc) |
CS6 |
CS6 |
DSCP-based |
CBWFQ |
|
Streaming video |
CS4 |
CS4 |
DSCP-based |
CBWFQ |
|
Voice/Video signaling (SIP, etc) |
CS3 |
CS3 |
DSCP-based |
CBWFQ |
|
Network management traffic (SNMP etc) |
CS2 |
AF21 |
DSCP-based |
CBWFQ |
|
Scavenger traffic |
CS1 |
CS0 |
DSCP-based |
CBWFQ |
|
Unclassified traffic |
CS0 (BE) |
CS0 |
DSCP-based |
CBWFQ |
The following example configuration outlines an implementation on the edge router of the network. The voice traffic is given a LLQ of 25% of the available bandwidth.
-
Make class maps to match network traffic on the edge router.
Start in privileged exec mode:
configure terminal class-map match-any voice match ip dscp ef class-map match-any bulk-data match ip dscp af11 match ip dscp af12 match ip dscp af13 class-map match-any transactional match ip dscp af21 match ip dscp af22 match ip dscp af23 class-map match-any mission-critical match ip dscp af31 match ip dscp af32 match ip dscp af33 class-map match-any routing match ip dscp cs6 class-map match-any voice-signaling match ip dscp cs3 match protocol sip class-map match-any net-management match ip dscp cs2 exit
-
Make policy-maps that can handle the reclassification, queuing, and dropping.
Note:
The class voice-media and voice-signaling together get 25% priority (21+4).From the global configuration mode:
policy-map qos-policy class voice- priority percent 21 class bulk-data bandwidth percent remaining 20 set ip dscp af22 random-detect dscp-based class transactional bandwidth percent remaining 15 set ip dscp af32 class mission-critical bandwidth percent remaining 30 set ip dscp af32 class routing bandwidth percent remaining 5 set ip dscp cs6 class voice-signaling priority percent 4 set ip dscp cs3 class net-management bandwidth percent remaining 5 set ip dscp af21 class class-default set ip dscp 0 random-detect dscp-based
-
Associate the policy to the WAN interface.
This example uses a serial link running at T1 speed.
From the global configuration mode:
interface serial 1/0 bandwidth 1544 service-policy output qos-policy
Call Admission Control (CAC)
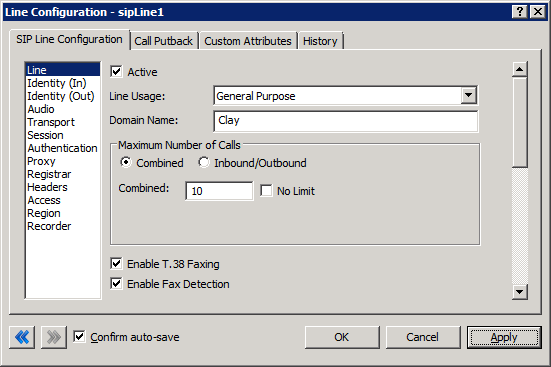
CIC has built-in Call Admission Control on the SIP Line. You can use it in situations where you must limit the number of calls that the system places. Adding just one more call can degrade the voice quality of all the other active calls when there is not sufficient bandwidth to support it. The following example shows that we have limited the CIC server to have a maximum of 10 calls associated with this SIP line. This setting does not account for bandwidth. The person doing the implementation must plan for the codec type and layer 2 overheard required.
Note:
CIC cannot guarantee the bandwidth needed for other activities on the WAN
in this configuration.