- Contents
PureConnect Release Notes
Enterprise Class Scalability & Management
CIC as a Pure Application Server
CIC version 4.0 eliminates the need for third-party voice hardware or HMP software. The Interaction Media Server appliance can now handle all CIC audio processing needs. The Interaction Media Server was developed for high volumes of audio processing and supports an NxM architecture. This means that when a single Media Server isn't sufficient for the size of the organization, a second or third Media Server can be deployed.
The Interaction Media Server's high-volume processing includes:
-
Compression/Encryption
-
Prompts and DTMF (IVR)
-
Call analysis
-
Fax
-
Conference
-
Speech Analytics / Word Spotting
By shifting the heavyweight audio operations from the CIC server to Media Servers, the CIC server can concentrate and focus on ACD routing, generation of reporting data, and all the other tasks that the server needs to perform. With audio operations removed from the CIC server, the scalability numbers for the overall platform have significantly improved over prior CIC releases.
The use of Interaction Media Servers also enhances system continuity, with the option to take selected Interaction Media Servers out of service for maintenance without impacting system performance. Multiple Media Servers can be used with a single CIC server, ensuring that in case of an issue or problem with one of the Media Servers, the other available Media Servers can continue handling telephone calls.
Significant architectural changes were made to support multiple locations - this feature is referred to as regionalization. Locations can be configured in CIC, and then each device and user configured on the server can be associated with a location. When a resource is required, for example -- a Media Server is needed for audio processing, CIC uses the Media Server closest to the device, eliminating or reducing the use of WAN capacity. The CIC solution can be deployed and architected around existing network topology. Gateways and other configured devices which are part of the CIC solution are now all location-aware. The use of these devices throughout the locations is configured in Interaction Administrator.
Session Manager Regionalization
An earlier version of CIC introduced the ability to install a Session Manager on a separate server for scalability purposes (off-server Session Manager). Multiple off-server Session Managers (OSSM) could be deployed in large scale environments. We have taken this concept to the next level and have now also introduced regionalization for off-server Session Managers. An OSSM is assigned to a specific region/location and all the client applications (Interaction Client and Interaction Center Business Manager) running in that location will now use the local OSSM.
As an example, a customer with two locations, each with 100 users, can now put an OSSM in each location servicing the local client applications. Instead of having 100 client applications in the remote location connecting to the Session Manager on the CIC server and using WAN bandwidth, these clients will now connect to the local Session Manager. This Session Manager in the remote location has one connection back to the CIC server to receive and send updates about all activities happening on the CIC server. The Session Manager distributes all the messages and information to all its connections, saving a huge amount of network traffic.
Easier and Improved Security Management
The user interface for security configuration and management in Interaction Administrator has changed significantly, allowing simplified management of these security settings. With the addition of a search function and the ability to get better insight into the security inheritance model, administration and ongoing system maintenance has become much easier. There are several new security settings that allow more granular control over existing features. The following paragraphs describe some of these changes in more detail.
Access Control
One of the biggest complaints from CIC administrators and other people responsible for configuring security settings in Interaction Administrator was the large number of drop-down lists. A system administrator had to go through a number of lists, each with several settings, to configure security settings or to determine the actual settings. CIC 4.0 eliminates that issue with the Access Control View, which is a single dialog box containing all the Queue Access Control settings. In this dialog box, CIC 4.0 now provides access to all access control settings without requiring the system administrator to scroll through a large number of lists.
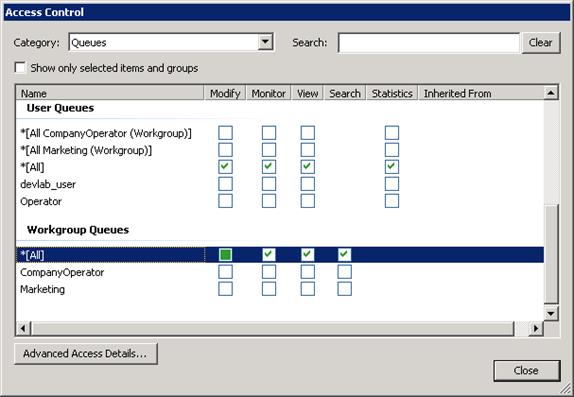
Queues Access Control
As shown in Figure above, the Modify and View rights can now be viewed side by side in a single dialog. System administrators can immediately see the existing configuration, making the maintenance of security rights much easier.
Another significant change around access control rights is the breakdown or more granular control of the View and Modify rights. In CIC 3.0, it was possible to grant someone View and/or Modify rights but there was no ability to control what features were included in that definition. In CIC 4.0, access control rights are more granular and allow configuration of which specific features are available through the Advanced Access Details options. See Figure for the Access Control Details dialog.
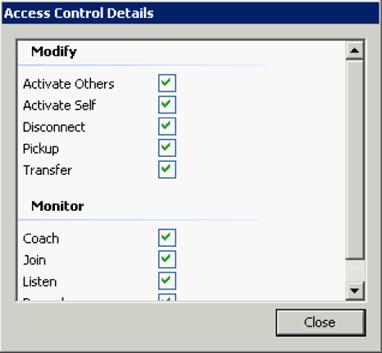
Access Control Details dialog box
Instead of just giving a user Modify rights to a particular user or queue, it is now possible to specify more details and control a user's rights by function.
Modify rights (for an ACD Workgroup) contain the following rights:
-
Activate Others
-
Activate Self
-
Disconnect
-
Pickup
-
Transfer
A new type of access right has been added around Monitoring. In the same way Modify Rights will be configured, there is a new set of Monitor Rights that contains the following rights:
-
Coach
-
Join
-
Listen
-
Record
In addition to the changes described above, CIC 4.0 introduces several new access control rights:
|
Access Control |
Description |
|
User Statistics |
Allows access to user statistics |
|
Change User Status |
Allows access to change a user's status |
|
Monitor |
Allows control to record, listen, join, and coach for user, workgroup, station and line queue |
|
Workgroup Statistics |
Allows control of workgroup statistics |
|
View in Search |
Allows control over which objects appear in Transfer Dialog Search |
|
Attendant Profile Search |
Allows access to attendant profiles in Transfer Dialog Search |
|
Status Column |
Allows access to status columns for a specific user in Interaction Client |
Display Inheritance Model
The security model in CIC is built around a specific inheritance model. A user's security rights are equal to the sum of all the rights given through the default user, roles, and workgroups, based on membership and the individual user level. In CIC 3.0 and prior releases, the administrator could see in Interaction Administrator that a specific user inherited specific security rights, but there was no method to see the source of the inherited rights. System administrators had to look at all possible objects to find the actual object that gave the user access to the feature through its inheritance model. In CIC 4.0, a column in the Interaction Administrator user interface indicates the objects from which a specific security right was inherited.
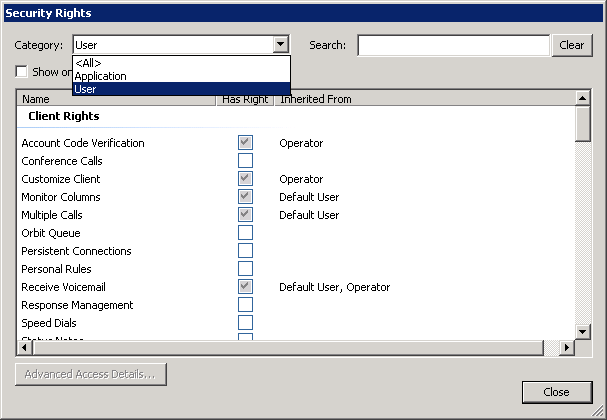
Showing 'Inherit From' when viewing user security rights
As shown in Figure , the user inherited the Receive Voicemail security right from the default user and the workgroup operator. This feature significantly reduces the amount of time it takes for a system administrator to set up and maintain their system.
Additional Security Rights
Several new security settings are now configurable in Interaction Administrator. Many of these security settings control access to features that were present in prior releases but that did not have configuration options in Interaction Administrator.
|
Security Right |
Description |
|
Personal Rule |
Allows access to Personal Rules from Interaction Client |
|
Response Management |
Allows access to the Response Management option in Interaction Client |
|
Orbit Queue |
Allows user to place objects in an orbit queue |
|
Workgroup/Profile Tab |
Allows user access to workgroup/profile information |
|
Tracker |
Allows access to Interaction Tracker from within Interaction Client |
|
Coach Interaction |
Allows the user to coach someone |
|
Conference Calls |
Allows the user to create a conference call |
|
Speed Dials |
Allows the user to create a speed dial page in Interaction Client |
|
Status Notes |
Allows the user to set status notes |
|
Park Interaction |
Allows the user to park an object |
Search Capability
When configuring systems with a large number of users, workgroups, and roles, it can sometimes be challenging to find the correct object. An earlier screenshot references the search feature added to the user interface. This option allows a user to search and filter the list with available objects based on custom search criteria, eliminating the need to scroll through long lists to find the desired user, workgroup, or role. As soon as a user starts typing the name of a workgroup or user, the resulting list displays only information that matches the search criteria.
Virtualization
CIC 4.0 supports virtualization of the CIC environment. For the latest information, see the CIC Virtualization Technical Reference in the PureConnect Documentation Library.
The CIC Virtualization Technical Reference provides best practices and strategies for successfully deploying Interactive Intelligence products on a virtualized platform, and applies to Microsoft Hyper-V and VMWare servers. The document lists Interactive Intelligence products that are currently supported, as well as not supported, for virtualization.
Concurrent Licensing
CIC 4.0 adds support for concurrent licensing. Concurrent licensing is supported for licenses that apply to users. The assigned license model in CIC 3.0 is still available.
CIC 4.0 offers two different types of licenses:
Assigned (or named) - This is the current model (CIC 3.0 and earlier) whereby a license is assigned to a user and is consumed even if the user is not logged in. You must have one license for each user to which you want to assign the license.
Concurrent license - This is a new license option in CIC 4.0. The license is assigned to a user but isn't consumed until the user logs in. In the concurrent license model, the license can be assigned to more users than there are licenses available; however the number of users who can log in is limited by the total number of concurrent licenses. For example, ten concurrent Contact Center Level 1 (CC1) licenses could be assigned to 100 users. Only the first ten users will be able to log in and get a CC1 license. The 11 th user will fail to acquire the license.
Assigned and concurrent licensing can be mixed on a single CIC server with the limitation that a single user must use either the concurrent or assigned mode. It is not possible for a single user to mix the two modes.
The concurrent version of a license is available on the 4.0 price sheet and appears immediately after the assigned license. Both licenses have the same name with the concurrent license having the suffix "- Concurrent." The concurrent licenses are also available in the online ordering system. Be aware that the part numbers for concurrent licenses differ from the assigned license part numbers.