- Contents
Interaction Desktop Help
Callback Window
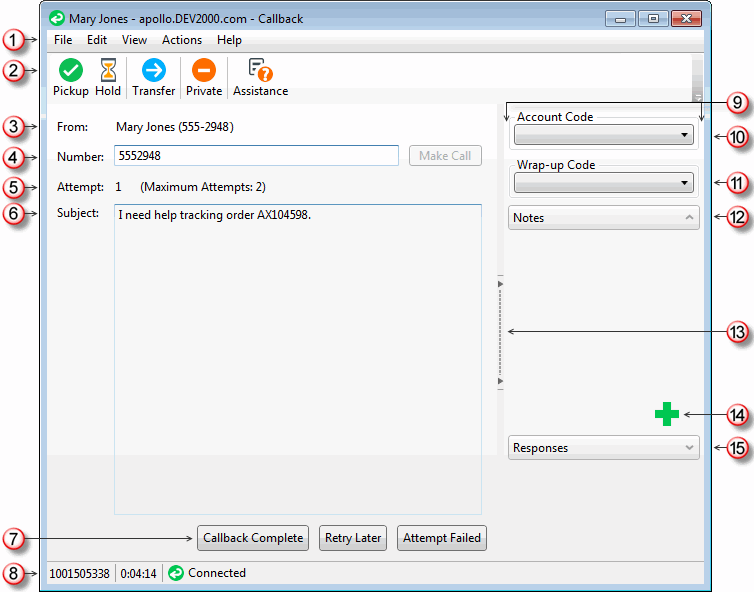
The Callback window appears when you pick up a callback request.
Tip: If you prefer not to see the sidebar view, click the splitter bar to collapse that portion of the Callback window.
|
1 |
Use these menus to perform various actions during a callback. |
|
|
2 |
The toolbar contains buttons for most of the functions for managing a callback request. Tip: Keyboard shortcuts are also available for these functions and are listed on the View menu. |
|
|
3 |
The name of the person who requested that someone call them back. |
|
|
4 |
The telephone number supplied by the person who requested the callback. Clicking the Make Call button dials the telephone number. |
|
|
5 |
If your CIC administrator enables the Retry Later feature, this displays the number of calls attempted in response to the callback request and the maximum number of attempts allowed. |
|
|
6 |
This area displays the reason the callback was requested. This information is usually required as a part of the process for requesting a callback. |
|
|
7 |
|
After you make the requested call, use these buttons to indicate whether you reached the requester or not. For more information, see Respond to a Callback Request. |
|
|
Click the Callback Complete button to indicate you reached the requester and completed the callback interaction. Note: This action disconnects only the callback interaction. You must disconnect the call interaction separately. |
|
|
|
The Retry Later button appears only if your CIC administrator has enabled this feature. The CIC administrator also configures the maximum number of times agents can retry a callback request. Click this button to remove the callback request from your queue and place it back on the workgroup queue in a "System" state. After the Snooze Time elapses, CIC transfer the callback request back to the workgroup queue. After this transfer, server parameters and handler customization can affect how the snoozed callback request is reprocessed. For more information, contact your CIC Administrator. |
|
|
|
Attempt Failed |
Click the Attempt Failed button to indicate that you cannot complete the callback request. It could be that the phone number is incorrect or that no one answered after the last allowed attempt. Tip: If your CIC system is appropriately configured, you may be able to select a Wrap-Up code that explains the reason for this failure. |
|
8 |
The Status bar displays the ID number, duration and state of the interaction. For more information, see Queue Contents. |
|
|
9 |
The appearance of the sidebar area can vary based on your user rights. It contains controls and information that are related to the callback request. |
|
|
10 |
Some companies categorize interactions by customer. If you have the appropriate rights, you can assign an Account code to the callback interaction. For more information, see Understanding Account Codes and Assign Codes to an Interaction. |
|
|
11 |
If you are a member of a workgroup for which Wrap-Up codes are configured, you can use this drop-down list to assign a Wrap-Up code to the callback interaction. For more information, see Understanding Wrap-Up Codes and Assign Codes to an Interaction. |
|
|
12 |
Use the Notes section to add notes or comments about the callback request. For more information, see Add Notes to an Interaction. Note: These notes are visible to other CIC client users who are "Listening to" (monitoring) this callback request. After the callback request is disconnected, these notes can be available in the Notes section of the Related Items view if the callback requester is identified and the Customer Interaction Center system collects this information. For more information, see your CIC administrator. |
|
|
13 |
If you prefer not to see the sidebar area, click the splitter to hide that part of the Chat window. Click the splitter again to restore the sidebar area. |
|
|
14 |
To add a note about the callback request, click this icon to open the Notes text box. For more information, see Add Notes to an Interaction. |
|
|
15 |
Select a pre-defined response. For more information, see Use Response Management for an Incoming Interaction. |
Related Topics